Curious about computer hardware? Wondering, What is an expansion slot. An expansion slot is similar to a doorway for increasing the power of your computer. It’s a motherboard socket that allows you to install additional parts, like sound or graphics cards. Explore the limitless possibilities once you unlock the potential of your device!
Table of Contents
What is an expansion slot?
An expansion slot is like a special socket on a computer’s motherboard that allows you to add extra features or capabilities to your computer. It’s kind of like having a spare space where you can plug in a new piece of hardware, such as a graphics card, sound card, or network card.
These added cards can give your computer more functions, like better graphics or improved sound. Think of it as a way to customize and upgrade your computer by simply plugging in new components.
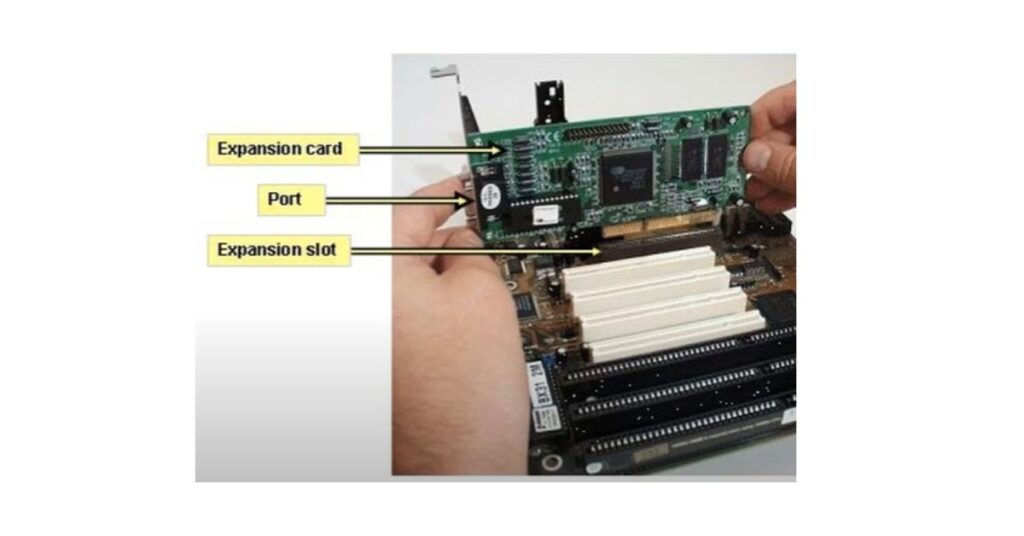
Types of Expansion Slots
Here are the different types of expansion Slots:
1: PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect)
PCI, which stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect, is a type of expansion slot on a computer’s motherboard. It’s like a connection point that allows you to add extra components to your computer for enhanced functionality.
Common uses
PCI slots are commonly used for various expansion cards, such as sound cards, network cards, and additional USB ports. They act as a kind of gateway for these cards to connect directly to the motherboard.
Advantages and limitations
- Advantages:
- Versatility: PCI slots are versatile and can support a range of different expansion cards, providing flexibility for users.
- Compatibility: Many older devices and cards are designed to work with PCI slots, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of hardware.
- Limitations:
- Speed: PCI has slower data transfer rates compared to newer technologies like PCIe, limiting the performance of high-bandwidth devices.
- Limited Bandwidth: The shared bandwidth among multiple PCI slots on the same bus can lead to limitations when several cards are installed simultaneously.
- Phasing Out: As technology advances, PCI is becoming less common in newer computers, with PCIe taking its place for faster and more efficient data transfer.
2: PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express)
PCIe, or Peripheral Component Interconnect Express, is an advanced type of expansion slot found on modern computer motherboards. It’s a technology that allows for high-speed communication between the motherboard and various components, enhancing the overall performance of a computer.
Characteristics
- Speed: PCIe offers significantly higher data transfer rates compared to its predecessor, PCI. This increased speed allows for faster communication between the motherboard and expansion cards.
- Lanes: PCIe uses a lane-based system, where each lane represents a pathway for data transfer. Common configurations include x1, x4, x8, x16, and x32, with larger numbers indicating more lanes and higher potential data transfer rates.
- Scalability: PCIe is scalable, meaning you can use different lane configurations to meet the bandwidth requirements of specific devices. This scalability contributes to its versatility in supporting various hardware components.
- Backward Compatibility: PCIe is designed to be backward compatible, allowing newer PCIe cards to work in older PCIe slots, albeit at the speed of the older slot.
Versions and Differences:
- PCIe 1.0 and 2.0: These earlier versions provided data transfer rates of 2.5 GT/s (Giga transfers per second) and 5 GT/s, respectively.
- PCIe 3.0: Introduced in 2010, PCIe 3.0 doubled the data transfer rate to 8 GT/s, enhancing performance.
- PCIe 4.0: Released in 2017, PCIe 4.0 doubled the data transfer rate again to 16 GT/s, providing even faster communication between the motherboard and expansion cards.
- PCIe 5.0: Released in 2019, PCIe 5.0 doubled the data transfer rate once more to 32 GT/s, making it the latest high-speed standard as of my knowledge cutoff in January 2022.
- PCIe 6.0: Announced in 2021, PCIe 6.0 is expected to offer further improvements in data transfer rates, aiming for 64 GT/s.
3: AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port):
AGP, or Accelerated Graphics Port, was a specialized type of expansion slot designed primarily for connecting graphics cards to a computer’s motherboard. It emerged in the late 1990s as a dedicated interface to address the increasing demands of graphics-intensive applications and games.
Designed Purpose
- Graphics Performance: AGP was specifically engineered to enhance graphics performance by providing a dedicated and faster pathway between the graphics card and the system memory.
- Data Transfer Rates: AGP allowed for high-speed data transfer rates between the graphics card and the motherboard, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall graphical processing capabilities.
- Advanced Features: AGP introduced features like sideband addressing and increased bus width, further optimizing the communication between the graphics card and the rest of the system.

Few other types of expansion slots
- ISA (Industry Standard Architecture): ISA was one of the earliest expansion slot types, commonly found in early personal computers. It featured a 16-bit bus and was used for various add-on cards such as sound cards and network adapters.
- EISA (Extended Industry Standard Architecture): EISA was an enhanced version of the ISA slot, featuring a 32-bit bus and backward compatibility with ISA cards. It aimed to provide faster data transfer rates and increased functionality.
- VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association): VESA Local Bus (VLB) was a short-lived expansion slot standard that emerged in the early 1990s. It provided a high-speed connection for graphics cards, aiming to improve video performance.
- CNR (Communication and Networking Riser): CNR was a type of slot designed for communication and networking devices. It allowed for the integration of audio, modem, and networking functions into a single expansion card.
- AMR (Audio/Modem Riser): AMR was similar to CNR but focused specifically on integrating audio and modem functions into a single card. It aimed to reduce manufacturing costs and simplify system integration.
These different types of expansion slots, which each catered to particular needs and technological advancements during their respective eras, played significant roles in the evolution of computer architecture. However, because of its great performance, scalability, and versatility, PCIe is mostly used for expansion in modern computers.
How can I find out what expansion slots are on my computer?

To find out what expansion slots are on your computer, you can:
- Check the Documentation: Refer to your computer’s user manual or motherboard documentation. It often provides detailed information about the types and locations of expansion slots.
- Inspect the Motherboard: Open your computer case and physically inspect the motherboard. Expansion slots are usually visible and labeled. Common types include PCIe slots, and PCI slots, and older systems may have AGP or other specialized slots.
- System Information Utility: Use the system information utility on your operating system. On Windows, you can type “System Information” in the search bar, and on macOS, you can find this information in “About This Mac” > “System Report.”
- Device Manager (Windows): In the Device Manager on Windows, you can expand the “System devices” category, and the entries related to your motherboard may provide details about the available expansion slots.
- Third-Party Software: Some third-party software, like CPU-Z, can provide detailed information about your system’s hardware, including the types of expansion slots available.
Can I upgrade expansion slot on my computer?
Unfortunately, your computer’s expansion slots cannot be upgraded. The physical layout and specifications of the motherboard dictate the kinds and quantity of expansion slots. It would be necessary to swap out the entire motherboard for one with the appropriate slot configuration in order to upgrade the expansion slots.
Generally speaking, you would need to think about upgrading your entire motherboard if you discover that you require more or different kinds of expansion slots. But this can be a difficult task, and compatibility issues with other parts of your system might also come up. Before making any significant hardware upgrades to your computer, always seek professional advice or consult the documentation.
Are there extension slots on laptops?
No, unlike desktop computers, traditional laptops usually do not have expansion slots. Because laptops are meant to be small and portable, adding more hardware is not always possible. Nevertheless, certain laptops might feature exclusive ports or connectors for particular expansion choices, like external GPUs or docking stations.
Final thoughts
An expansion slot is a socket on the motherboard of a computer made to hold expansion cards. These add-on cards expand the capabilities of a computer by adding features like networking, graphics, audio, and storage. By serving as connecting points, expansion slots let users improve and personalize their systems. Different slot types have developed over time, including PCI, PCIe, AGP, and others, each with unique benefits and drawbacks.
Expansion slots are necessary for increasing a computer’s functionality, but it’s important to make sure the expansion card fits the slot correctly and take compatibility, size, and power requirements into account.
