At the core of every computer system lies a crucial component known as the motherboard. Serving as the central nervous system, the motherboard connects and facilitates communication between various hardware components, such as the processor, memory, and storage devices.
This vital piece of technology is aptly named the “motherboard” as it houses and nurtures the essential elements that make your computer function seamlessly. To demystify the question, “What is a Motherboard?” is to unveil the intricate web of connections and functionalities that make this electronic mainboard the cornerstone of computing prowess. Explore the intricate details and significance of the motherboard, delving into the heart of your computer’s functionality.
Table of Contents
What is a Motherboard?
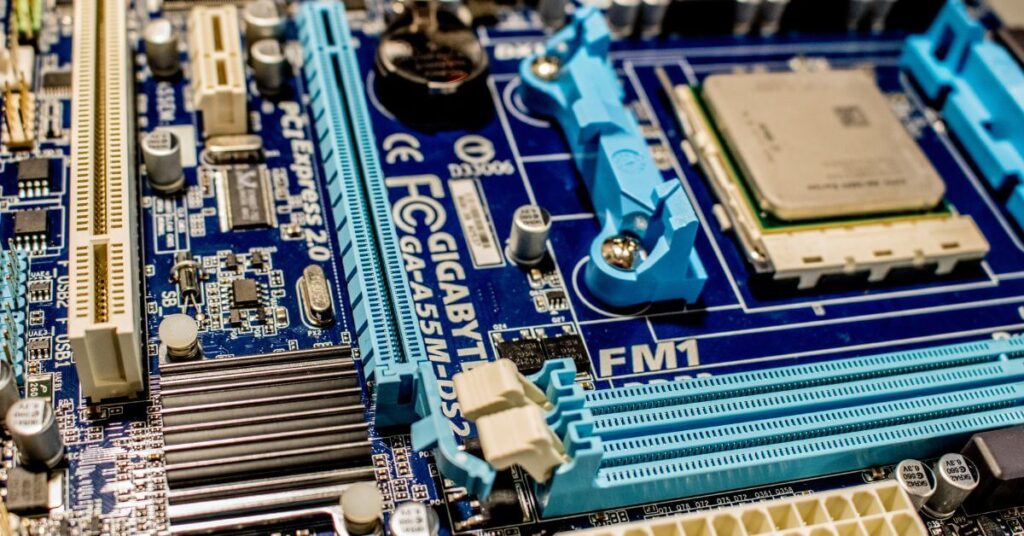
A. Definition of a Motherboard
The motherboard, often referred to as the mainboard or system board, serves as the primary circuit board of a computer. It provides the foundation for connecting all essential components, fostering communication between them to execute complex tasks.
B. Importance in Computing
As the backbone of a computer, the motherboard integrates the central processing unit (CPU), memory, and other critical elements. Its design directly influences system performance, making it a vital consideration for both casual users and gaming enthusiasts.
C. Evolution of Motherboards
From the rudimentary designs of early computers to the intricately engineered modern variants, motherboards have evolved significantly. Understanding this evolution provides insight into the rapid advancements in computing technology.
Further reading: Who found The Motherboard?
Components of a Motherboard
A. Central Processing Unit (CPU) Socket
The CPU socket, a key feature on the motherboard, determines the compatibility of the chosen processor. Different sockets accommodate various CPU architectures, emphasizing the need for careful selection.
B. Memory Slots
Memory slots house RAM modules, influencing the system’s multitasking capabilities and overall speed. Exploring the types and capacities of memory supported by the motherboard is crucial for optimal performance.
C. Expansion Slots
Expansion slots facilitate the connection of additional components like graphics cards, sound cards, and networking cards. Understanding the available slots and their specifications is essential for users seeking to enhance their system’s functionality.
D. Power Connectors
Power connectors on the motherboard ensure efficient distribution of electricity to all connected components. Examining these connectors aids in selecting a compatible power supply unit, promoting stability and reliability.
E. Input/Output Ports
The variety of input/output ports on a motherboard determines its connectivity options. Users should assess the availability and type of ports based on their peripheral devices and usage requirements.
Further reading: Why motherboard is important?
Types of Motherboards
A. ATX Motherboards
ATX motherboards, characterized by their standard size, offer a balance between features and expandability. Understanding the advantages and limitations of ATX form factor aids users in tailoring their systems to specific needs.
B. Micro ATX Motherboards
Micro ATX motherboards, with a smaller footprint, cater to compact builds without sacrificing essential features. Exploring the benefits of this form factor is crucial for users seeking a balance between performance and space efficiency.
C. Mini ITX Motherboards
Mini ITX motherboards, known for their diminutive size, are popular in small form factor (SFF) builds. Evaluating the trade-offs in terms of expandability and cooling solutions guides users in making informed choices.
D. Extended ATX Motherboards
Extended ATX motherboards, designed for enthusiasts and high-performance systems, offer additional expansion slots. Analyzing the compatibility with chassis and cooling solutions is vital for users planning elaborate setups.
Further reading: Micro ATX vs Mini ITX
Motherboard Form Factors
A. Understanding Form Factors
Form factors dictate the physical dimensions and layout of motherboards. Navigating the nuances of form factors enables users to choose a motherboard that aligns with their case and build preferences.
B. Impact on System Configuration
The chosen form factor significantly influences the overall layout and aesthetics of the computer system. Exploring its impact helps users create visually appealing and well-organized setups.
C. Popular Form Factors Explained
Delving into popular form factors like ATX, Micro ATX, and Mini ITX provides users with insights into the diverse options available. Each form factor caters to specific needs, emphasizing the importance of compatibility.
Further reading: Why Are Motherboards So Expensive?
Choosing the Right Motherboard
A. Compatibility Considerations
Ensuring compatibility with existing components and future upgrades is paramount. Users should meticulously assess specifications to avoid potential issues in system integration.
B. Performance Requirements
It is understanding the demands of intended usage, whether gaming, content creation, or professional applications, guides users in selecting a motherboard that meets their performance expectations.
C. Future Upgrade Potential
Anticipating future hardware upgrades is essential for a sustainable system. Choosing a motherboard with ample expansion options safeguards against obsolescence and facilitates seamless upgrades.
D. Budgetary Constraints
Balancing features and cost is crucial when choosing a motherboard. Users should weigh their budgetary constraints against the desired features to make an informed and cost-effective decision.

Further reading: Should You Replace A Motherboard Or Buy A New Computer?
Motherboard Chipsets
A. Definition and Role
Chipsets serve as the communication hub between the CPU, memory, and peripherals. Understanding their role elucidates how different chipsets impact system performance and functionality.
B. Popular Chipset Types
Exploring prevalent chipset types, such as Intel’s Z series or AMD’s B series, provides users with insights into each chipset’s specific features and capabilities.
C. How Chipsets Affect System Performance
The synergy between the motherboard chipset and other components significantly influences overall system performance. Users should grasp the nuances to optimize their computing experience.
BIOS and UEFI
A. Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)
The BIOS, a fundamental firmware interface, initializes hardware components during the system boot process. Examining its functions and limitations highlights the transition to more advanced alternatives.
B. Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)
UEFI, a modern replacement for BIOS, offers enhanced features such as graphical interfaces and secure boot options. Understanding the advantages of UEFI empowers users to leverage advanced functionalities.
C. Advantages of UEFI over BIOS
Comparing UEFI to traditional BIOS underscores the benefits, including faster boot times, improved security features, and a more user-friendly interface. Users can appreciate the advantages of this technological evolution.
Further reading: Motherboard vs Processor
Overclocking Capabilities
A. Understanding Overclocking
Overclocking involves pushing hardware components beyond their factory-set limits to enhance performance. Delving into the basics of overclocking sets the stage for exploring motherboard features that support this practice.
B. Motherboard Features for Overclocking
High-quality VRMs, effective cooling solutions, and robust power delivery systems are crucial for successful overclocking. Assessing these features guides users in selecting motherboards suited for overclocking endeavors.
C. Risks and Rewards of Overclocking
While overclocking can yield performance gains, it comes with inherent risks, including increased heat generation and potential hardware damage. Users should weigh the rewards against the risks before venturing into overclocking.
Further reading: What is the normal lifespan of a computer?
Motherboard Brands and Reviews
A. Top Motherboard Brands in the Market
Identifying reputable motherboard manufacturers ensures product reliability and customer support. Exploring the top brands in the market guides users toward trusted options.
B. Customer Reviews and Ratings
Real-world user experiences provide valuable insights into the performance and reliability of specific motherboard models. Users should consult reviews and ratings to make informed purchasing decisions.
C. Choosing a Reliable Manufacturer
Considering factors such as warranty, customer support, and brand reputation aids users in choosing a motherboard from a reliable manufacturer. Building a system with trusted components enhances long-term satisfaction.
Troubleshooting Common Motherboard Issues
A. Diagnosing Hardware Failures
Understanding common hardware failure symptoms facilitates efficient troubleshooting. Users should equip themselves with diagnostic tools and knowledge to address potential issues.
B. Addressing Connectivity Problems
Connection issues can impede system functionality. Exploring common connectivity problems and their solutions empowers users to resolve issues independently.
C. Software and Firmware Solutions
Updating drivers, BIOS, and firmware is essential for maintaining system stability. Users should implement regular software and firmware updates to address potential bugs and security vulnerabilities.
Future Trends in Motherboard Technology

A. Advancements in Connectivity
Rapid developments in connectivity standards, such as USB4 and PCIe 5.0, shape the future of motherboards. Understanding these advancements prepares users for upcoming innovations.
B. Integration of Emerging Technologies
The integration of technologies like Wi-Fi 6E and DDR5 memory heralds a new era in motherboard capabilities. Exploring these emerging technologies provides a glimpse into the future of computing.
C. Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Designs
Motherboard manufacturers increasingly focus on sustainable practices. Evaluating eco-friendly initiatives and materials used in manufacturing aligns with the growing emphasis on environmental responsibility.
Further reading: How to check motherboard drivers?
Case Studies: Motherboards in Custom Builds
A. Showcasing Successful Custom Builds
Examining case studies of custom builds highlights innovative implementations of motherboard features. Users can draw inspiration from these examples for their unique projects.
B. Unique Implementations of Motherboard Features
Enthusiasts often push the boundaries of creativity by utilizing motherboard features in unconventional ways. Exploring these unique implementations showcases the versatility of motherboards.
C. Tips from Enthusiasts and Professionals
Gaining insights from experienced enthusiasts and professionals offers valuable tips for optimizing motherboard performance. Users can benefit from the collective knowledge of the community.
Security Concerns with Motherboards
A. Vulnerabilities in Motherboard Designs
Motherboards are not immune to cybersecurity threats. Identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing security measures is essential for safeguarding sensitive data.
B. Protection Measures Against Cyber Threats
Utilizing features like secure boot and regularly updating firmware enhances the security posture of motherboards. Users should adopt proactive measures to mitigate potential cyber threats.
C. Importance of Regular Updates
Staying vigilant with updates is crucial for addressing security vulnerabilities. Regularly updating software, firmware, and security applications ensures the latest protections against evolving threats.
Environmental Impact of Motherboard Manufacturing
A. Raw Materials Used in Motherboard Production
Understanding the materials used in motherboard manufacturing sheds light on the environmental impact. Exploring sustainable material choices contributes to responsible consumer decisions.
B. E-Waste Management
As electronic waste continues to be a global concern, assessing motherboard disposal options and recycling programs becomes imperative. Responsible e-waste management is essential for minimizing environmental impact.
C. Sustainable Practices in Manufacturing
Highlighting manufacturers’ efforts toward sustainable practices encourages environmentally conscious consumer choices. Supporting companies with eco-friendly initiatives contributes to a greener technology landscape.
Further reading: Motherboard Vs Mainboard A Detailed Comparison
Interview with Motherboard Industry Expert
A. Insights into Current Trends
An interview with a motherboard industry expert provides firsthand insights into the latest trends shaping the market. Understanding current developments aids users in making informed decisions.
B. Predictions for Future Developments
Industry experts often offer predictions regarding future motherboard technologies. Exploring these predictions provides users with a glimpse into the evolving landscape of computer hardware.
C. Expert Recommendations for Consumers
Receiving recommendations from industry experts helps users navigate the myriad options available. Expert insights guide users toward making choices aligned with their specific needs and preferences.
Conclusion
A. Recap of Key Points
Summarizing key points reinforces the critical aspects users should consider when exploring motherboards. A concise recap enhances reader retention of essential information.
B. Final Thoughts on Motherboards
Concluding with reflections on the significance of motherboards in the broader computing context encapsulates the article’s central theme. Final thoughts leave a lasting impression on readers.
C. Encouraging Informed Consumer Choices
Empowering readers to make informed choices underscores the educational value of the article. Encouraging a proactive approach to motherboard selection enhances user satisfaction and confidence.
