What is a CPU socket? A CPU socket serves as the crucial interface between a central processing unit (CPU) and a computer’s motherboard. It’s a physical structure that allows the CPU to be securely attached, facilitating communication and power supply.
The socket type varies across different processor models and manufacturers, playing a pivotal role in determining compatibility between CPUs and motherboards. Understanding CPU sockets is essential for anyone building or upgrading a computer, as it influences hardware selection and system performance.
Table of Contents
What is a CPU socket?
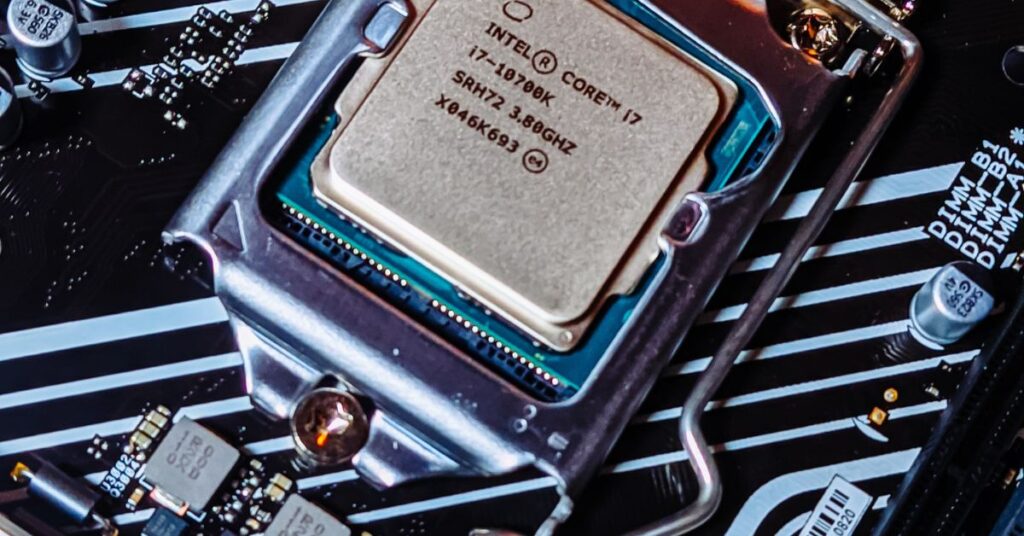

Think of a CPU socket as the connector that firmly and functionally hugs the motherboard, the central processing unit (CPU), and your computer’s brain together. It serves as the CPU’s residence and source of power as well as a conduit for communication with the rest of the computer. Consider it as a specific wall socket that supplies power and a communication channel between your CPU and the other components of your computer.
Here’s the thing: just like keys fit different locks, CPUs are available in a variety of sizes and shapes. The CPU is the special key that fits precisely into the CPU socket, which is like a lock. Therefore, you must ensure that the CPU key fits the socket lock on your motherboard when building or upgrading your computer. If you don’t follow the steps correctly, your CPU won’t be able to work its magic. It’s a compatibility dance. Thus, the next time you hear the term “CPU socket,” picture it as the comfortable opening through which the motherboard receives signals from your computer’s brain, enabling smooth operation of the entire system.
Importance of CPU sockets in computer architecture
Because they serve as a link between the motherboard, the central processing unit (CPU), and the computer’s brain, CPU sockets are crucial to computer architecture. The foundation of a computer’s functionality and performance is shaped by these sockets, which establish compatibility between CPUs and motherboards.
Think of CPU sockets as the matching puzzle board slots and CPUs as various puzzle pieces. Every CPU has a unique form, and the socket guarantees a reliable and safe connection by offering a channel for communication as well as power. When building or upgrading a computer, users need to consider compatibility. Selecting the appropriate CPU socket guarantees that the CPU and motherboard combine seamlessly, enhancing system performance as a whole.
Additionally, as technology advances, CPU socket designs adapt to accommodate modifications in processor architecture and features. CPU sockets play a more important role as CPUs become more complex and powerful, which affects a computer system’s overall potential and capability. CPU sockets are the cornerstone of computer architecture, allowing the motherboard infrastructure and the processing powerhouse to coexist harmoniously.
Types of CPU Sockets
CPU sockets come in various types, each designed to accommodate specific processor models. The diversity arises due to differences in CPU architectures, manufacturers, and technological advancements.
Some prominent CPU socket types include:
LGA (Land Grid Array)
- Description: LGA sockets feature a grid of pins on the motherboard and corresponding pads on the CPU. The processor sits atop these pads, creating a reliable electrical connection.
- Examples: Intel’s LGA 1200 for 10th and 11th Gen Core processors.
PGA (Pin Grid Array)
- Description: PGA sockets involve pins on the processor that directly plugs into the motherboard’s holes. The CPU is secured in place, and the pins establish the necessary connections.
- Examples: AMD’s AM4 socket for Ryzen processors.
BGA (Ball Grid Array):
- Description: In BGA sockets, the CPU is soldered directly onto the motherboard, making it a permanent part of the system. These are commonly found in devices like laptops and certain embedded systems.
- Examples: Many mobile processors and some low-power embedded CPUs.
LGA Server Sockets
- Description: Designed for server-grade CPUs, these sockets, such as Intel’s LGA 3647, cater to the specific requirements of high-performance computing environments.
TR4 and sTRX4
- Description: AMD’s TR4 and sTRX4 sockets are tailored for high-end desktop (HEDT) CPUs like the Ryzen Threadripper series, offering additional features and capabilities.
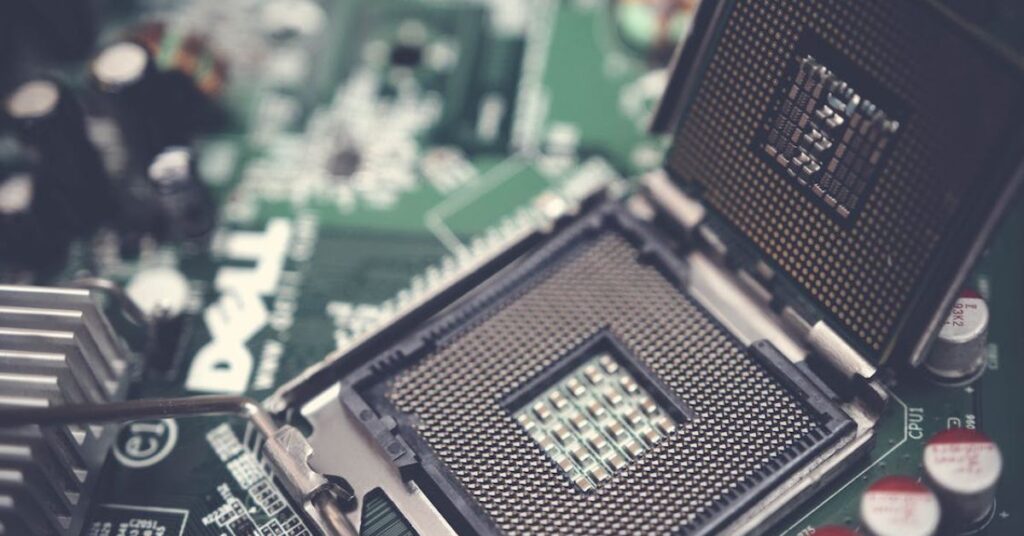
Evolution of CPU sockets over time
The evolution of CPU sockets over time reflects the rapid pace of advancements in computer technology. Over several decades, CPU sockets have significantly changed in design, architecture, and capabilities.
Here’s a broad overview of the evolution:
- Early Sockets (1970s-1980s): During the early years of personal computing, CPUs were often soldered directly onto the motherboard, and upgrading or replacing them was challenging. Socketed CPUs became more prevalent in the 1980s, allowing for easier maintenance and upgrades.
- PGA and Socket Variants (the 1990s-2000s): The 1990s saw the rise of Pin Grid Array (PGA) sockets, where CPUs had an array of pins plugged into corresponding holes on the motherboard. Intel’s Socket 7 (for Pentium and AMD K6 processors) and Slot 1 (for Pentium II) were prominent during this era.
- LGA Introduction (2000s): Intel introduced Land Grid Array (LGA) sockets with the Pentium 4, where the pins moved from the CPU to the socket. This change aimed to reduce the risk of bent pins and facilitate the manufacturing process.
- Socket Variety Expansion (2000s-2010s): Both Intel and AMD introduced various socket types to accommodate the diverse range of processors. Examples include Intel’s LGA 775, LGA 1366, and AMD’s Socket AM2, AM3, and FM2.
- Integration Challenges (2010s): Increasing integration of components onto the CPU, such as graphics and memory controllers, posed challenges. BGA (Ball Grid Array) sockets became common in laptops and certain low-power systems, where CPUs were soldered directly onto the motherboard.
- Advancements in Server Sockets (2010s): Server-grade CPUs witnessed the development of high-capacity sockets like Intel’s LGA 2011 and LGA 3647 to accommodate the demands of data centers and high-performance computing.
- HEDT Sockets (2010s-Present): High-end desktop (HEDT) CPUs, such as Intel’s Core X-Series and AMD’s Ryzen Threadripper, brought about specialized sockets like LGA 2066 and TR4/sTRX4, offering increased capabilities for enthusiasts and professionals.
- Continued Innovation (Present): Ongoing advancements in CPU architecture, manufacturing processes, and computing demands continue to influence socket designs. Manufacturers aim to balance performance, power efficiency, and compatibility, ensuring that new CPUs remain backward-compatible with certain older sockets.
Components of a CPU socket
Here are the components of a CPU socket:
1: Socket Housing
The exterior structure that houses and holds the CPU within the motherboard is called the socket housing. It gives the CPU alignment, structural support, and electrical insulation. Each socket type has a unique socket housing design that guarantees a good fit for the matching CPU.
2: Pins and Contact Points
The essential parts in charge of creating the electrical connections between the motherboard and CPU are pins and contact points. The CPU in PGA sockets has a range of pins that line up with holes in the socket. The pins in LGA sockets are found on the socket itself, forming contact points that make direct contact with the CPU’s pads.
3: Latching Mechanism
Many CPU sockets have a latching mechanism that helps to hold the processor firmly in place. When engaged, a lever or latch that firmly presses the CPU against the socket may be involved. A dependable electrical connection is made possible by this mechanism, which guarantees correct alignment and contact between the pins or contact points.
4: Thermal Solution Attachment Points
The socket’s thermal solution attachment points are places where the cooling solution—a heat sink or fan—is fastened to disperse heat produced by the CPU while it is operating. These are essential points to keep the CPU from overheating and to maintain ideal temperatures. The overall stability and longevity of the processor are enhanced by the thermal solution attachment points.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the CPU socket acts as a vital interface between the motherboard and processor, enabling physical support, electrical connections, and effective heat management. CPU socket evolution reflects a dynamic response to user needs and technological advancements.
Key components include the socket housing, pins, latching mechanism, and thermal solution attachment points. Users who are navigating the intricacies of building or upgrading a computer must have a thorough understanding of these components to ensure compatibility, optimal performance, and system longevity. The CPU socket continues to be an essential component that shapes computer architecture as computing technology advances.
FAQ
How do I know which CPU socket my motherboard supports?
Check your motherboard’s specifications in the user manual or on the manufacturer’s website. The CPU socket type will be mentioned. Match this with the socket type of the CPU you plan to use.
Can I upgrade my CPU without changing the motherboard?
It depends on the compatibility between the existing motherboard’s socket and the new CPU. If the sockets match, you can upgrade without changing the motherboard. Otherwise, you may need to replace both.
What’s the difference between PGA and LGA sockets?
In PGA (Pin Grid Array) sockets, the CPU has pins that plug into the motherboard. In LGA (Land Grid Array) sockets, the pins are on the motherboard, and the CPU has contact pads. LGA sockets often reduce the risk of bent pins.
Why do CPUs have different socket types?
CPU manufacturers develop different socket types to accommodate variations in CPU architectures, power requirements, and technological advancements. It allows for flexibility and specialization in the ever-evolving landscape of computer hardware.
Are CPU coolers universal, or do they depend on the socket type?
CPU coolers often depend on the socket type. Different sockets may require specific mounting mechanisms. Always check the compatibility of the cooler with your CPU socket before purchasing.
What’s the purpose of the latching mechanism on a CPU socket?
The latching mechanism secures the CPU in place, ensuring proper alignment and contact between pins or contact points. This helps establish a reliable electrical connection between the CPU and the motherboard.
Can I use a thermal solution from a different manufacturer with my CPU socket?
It depends on compatibility. Many coolers come with adapters for various socket types, but it’s essential to check that the thermal solution is compatible with your CPU socket before installation.
