Embarking on the intricate journey of electronic wonders, we unravel the enigma of “Motherboard vs. Circuit Board.” These titans of technology often spark curiosity, but what sets them apart? Picture a symphony of silicon orchestrating your device’s every move, and you’re diving into the realm of motherboards.
Contrast that with the humble circuit board – the unsung hero weaving connections in the background. In this electronic showdown, we decipher the nuances, demystify the jargon, and explore the heartbeat of your gadgets. Join us in unraveling the web of wires, chips, and innovation, as we unveil the captivating tale of Motherboard vs. Circuit Board.
Table of Contents
Motherboard vs. Circuit Board
In the grand symphony of electronics, the motherboard takes center stage, adorned with connectors for vital peripherals – CPU, RAM, and hard disk. This technological maestro also boasts expansion slots, welcoming additional components like graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards into its ensemble. It stands tall as the primary circuit board orchestrating a computer’s every move.
On the flip side, the circuit board, also known as a printed circuit board (PCB), dances to a different rhythm. Utilizing conductive “traces,” it weaves intricate connections for the essential components like resistors and capacitors. This elegant dance of electrons is the backbone of electronic marvels, from TVs and radios to the ubiquitous smartphones we can’t live without. Motherboard vs. Circuit Board: different roles, but both integral to the magic of technology.
Motherboard vs. Circuit Board: Comparing with a Table Format
| Aspect | Motherboard | Circuit Board (PCB) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Main circuit board in a computer, connecting essential components like CPU, RAM, and storage devices | Backbone of electronic devices, facilitating connections for resistors, capacitors, and other components |
| Connectors | Features connectors for peripherals and expansion slots for additional components | Utilizes conductive “traces” to connect components required for electronic products |
| Role | Orchestrates the overall functioning of a computer system | Fundamental in enabling the functionality of devices such as TVs, radios, and smartphones |
| Components Supported | CPU, RAM, hard disk, expansion slots for graphics cards, sound cards, network cards, and more | Resistors, capacitors, and various electronic components necessary for device operation |
| Application | Central hub in computers, supporting a range of add-ons for customization | Essential in the manufacturing of electronic products, providing the foundation for functionality |
| Importance | Crucial for the seamless operation of a computer system | Fundamental in the production of electronic devices, serving as the core infrastructure |
It’s time for a thorough, detailed comparison now.
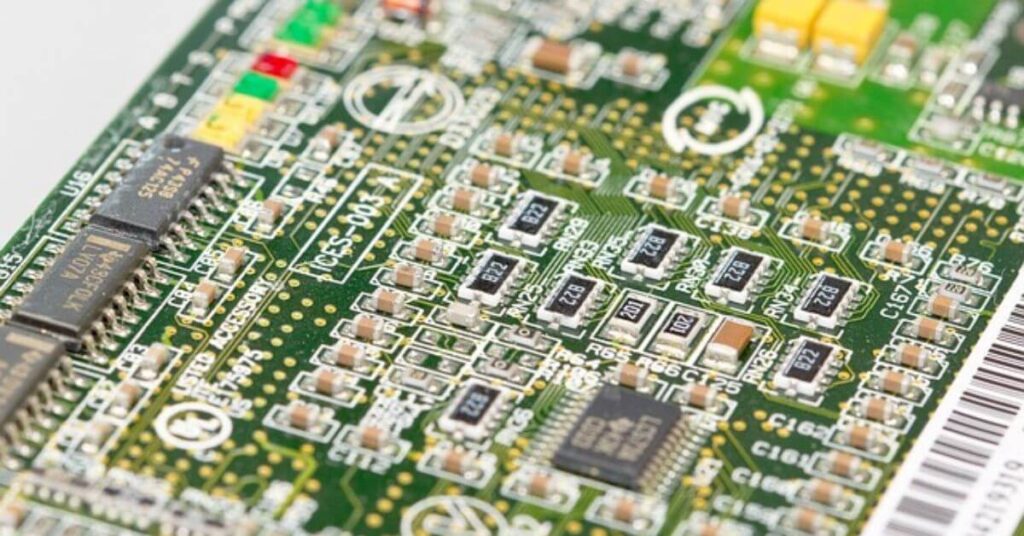
Function
Motherboard: The motherboard is the central nervous system of a computer, playing a pivotal role in connecting and facilitating communication between various essential components. Its primary function is to serve as the main circuit board, linking the CPU, RAM, and hard disk. Additionally, it provides expansion slots for peripherals such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards, thereby enabling customization and enhancing the computer’s capabilities.
Circuit Board (PCB): In contrast, a circuit board, or printed circuit board (PCB), is designed with a more specific purpose. Its function revolves around providing a platform for the connection of electronic components like resistors and capacitors. These conductive “traces” on the PCB create pathways for electrical signals to flow, allowing the integrated components to work in harmony.
Further reading: What Is The Normal Lifespan Of A Computer?
Components
Motherboard: The motherboard supports a diverse array of components crucial for a computer’s functionality. These include the central processing unit (CPU), random access memory (RAM), and storage devices. Expansion slots on the motherboard accommodate additional components such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards, contributing to the system’s overall performance and capabilities.
Circuit Board (PCB): On the other hand, a circuit board focuses on supporting the electronic components necessary for specific devices. These components typically include resistors, capacitors, and other elements critical for the operation of electronic products like TVs, radios, and smartphones.
Size
Motherboard: Motherboards are relatively larger compared to individual circuit boards. The larger size is necessary to accommodate the numerous connectors, slots, and ports required to link various components and peripherals within a computer system.
Circuit Board (PCB): Circuit boards come in a variety of sizes, tailored to the dimensions of the devices they are intended to support. They are more compact, emphasizing efficiency and space utilization in the context of specific electronic products.
Importance
Motherboard: The motherboard holds paramount importance in the realm of computing. It is the backbone of a computer system, dictating its overall performance and capabilities. A well-designed and robust motherboard can significantly impact the user experience, making it a critical component in the world of technology.
Circuit Board (PCB): The importance of circuit boards lies in their ubiquity across electronic devices. Without PCBs, the intricate circuitry needed for devices like TVs, radios, and smartphones to function seamlessly would be unattainable. They are the unsung heroes that enable the smooth operation of our everyday electronic gadgets.
Role
Motherboard: The motherboard takes on the role of an orchestrator, managing data flow and instructions between various components. It ensures that the CPU can communicate effectively with the RAM, storage devices, and other peripherals, creating a cohesive computing environment.
Circuit Board (PCB): The circuit board assumes the role of a foundation, providing the necessary infrastructure for electronic components to connect and collaborate. It acts as a conductor, allowing electrical signals to traverse the intricate pathways and create the desired functionalities within electronic devices.
Cost
Motherboard: Motherboards tend to be relatively more expensive due to their comprehensive functionality and the multitude of features they offer. The cost may vary based on factors such as brand, specifications, and additional features.
Circuit Board (PCB): Circuit boards, being more specialized and tailored to specific devices, may have a lower individual cost. Factors like size, and complexity influence the cost of PCBs, and the specific electronic components integrated into the board.
Can a circuit board replace a motherboard in a computer system?
No, a circuit board cannot replace a motherboard in a computer system. Motherboards are specifically designed to manage the entire system, while circuit boards, such as PCBs, are tailored for specific electronic devices. Their functions and capabilities are not interchangeable in the context of computing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricacies of technology bring to light the clear distinction between circuit boards and motherboards. While both play vital roles in the functionality of electronic devices, they are not interchangeable. The motherboard stands as the central hub in a computer system, orchestrating the communication between essential components and supporting a myriad of peripherals. On the other hand, circuit boards, particularly printed circuit boards (PCBs), serve as the fundamental building blocks for various electronic devices, providing the necessary infrastructure for components to collaborate.
In the grand tapestry of technology, understanding the nuanced differences between circuit boards and motherboards is key to appreciating their unique contributions. Motherboards take center stage in the computing world, while circuit boards quietly underpin the functionality of everything from TVs to smartphones. Together, they embody the essential components that drive innovation and power our electronic-driven lives.
Frequently ask question
What is the primary function of a motherboard?
The motherboard serves as the central circuit board in a computer, connecting vital components like the CPU, RAM, and storage devices. It also features expansion slots for additional peripherals, enhancing the computer’s capabilities.
What components are supported by a motherboard?
Motherboards support crucial components such as the CPU, RAM, and storage devices. They also include expansion slots for peripherals like graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards, allowing users to customize their systems.
What electronic products use circuit boards?
Circuit boards, particularly PCBs, are integral to a wide range of electronic products, including TVs, radios, smartphones, and other devices. They facilitate connections for components like resistors and capacitors necessary for the functioning of these devices.
Are motherboards and circuit boards the same size?
No, they differ in size. Motherboards are larger to accommodate various connectors, slots, and ports needed in a computer system. Circuit boards come in different sizes, tailored to fit the dimensions of specific electronic devices.
Why are motherboards generally more expensive than circuit boards?
Motherboards are more comprehensive, offering a wide range of features and functionalities for computer systems. The cost is influenced by factors like brand, specifications, and additional features. In contrast, circuit boards may have a lower individual cost as they are tailored to specific devices.
Can a device function without a circuit board?
In most cases, electronic devices cannot function without a circuit board. The circuit board, especially the PCB, provides the essential infrastructure for connecting electronic components, enabling them to work together seamlessly.
Do both motherboards and circuit boards contribute to the innovation of technology?
Yes, both play crucial roles in technology. Motherboards drive innovation in computing, offering platforms for advanced features and customization. Circuit boards, on the other hand, contribute to the innovation of electronic devices by providing the foundational structure for their functionality.
