Building or upgrading a computer can be an exciting venture, but it comes with its fair share of considerations. One crucial aspect is ensuring that your graphics card (GPU) is properly installed in the right motherboard slot.
We’ll go over the fundamentals of selecting the right PCIe motherboard slot for your GPU in this article. answering the question, Which motherboard slot for the GPU? When you’re a seasoned builder or a first-time PC enthusiast. Let’s get started and make this process straightforward and hassle-free.
Table of Contents
Types of Motherboard Slots
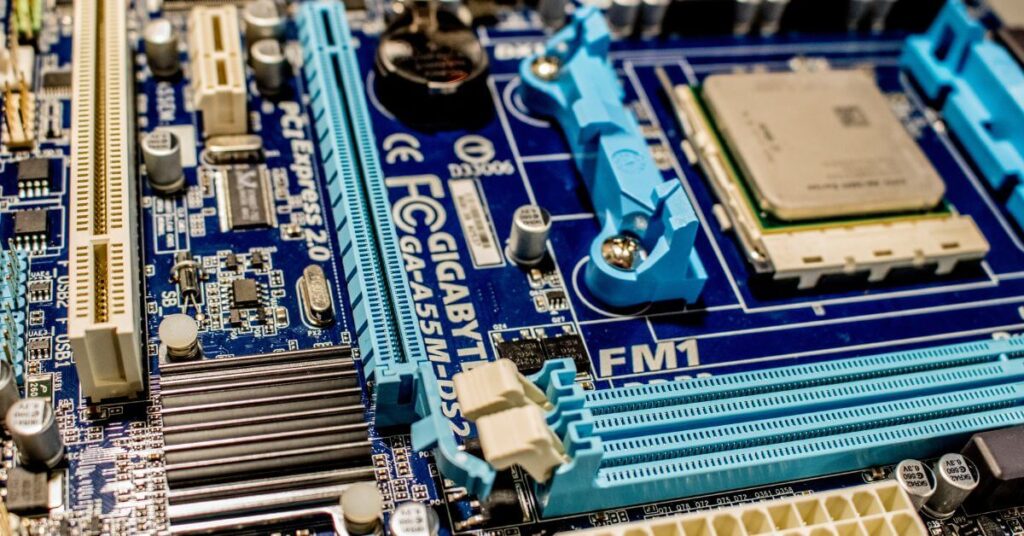
When it comes to connecting a graphics card (GPU) to your motherboard, the type of slot you use is crucial. Here are the primary types you should be familiar with:
PCI Express x16 (PCIe x16)
- Overview: This is the most common and widely used slot for GPUs. It provides high bandwidth, allowing for fast communication between the GPU and the rest of the system.
- Compatibility: Almost all dedicated graphics cards are designed to be installed in a PCIe x16 slot. It offers the necessary speed for modern GPUs.
PCI Express x8 (PCIe x8) and x4 (PCIe x4)
- Overview: These slots are less common for graphics cards but may be found on certain motherboards. While x8 and x4 slots offer lower bandwidth than x16, they can still accommodate less demanding GPUs or other expansion slots.
- Use Cases: PCIe x8 and x4 slots may be suitable for secondary GPUs, additional expansion cards, or non-demanding graphics tasks.
PCI Express x1 (PCIe x1)
- Overview: PCIe x1 slots are smaller and used for various expansion cards such as sound cards, network cards, or Wi-Fi adapters. They are not designed for graphics cards due to their limited bandwidth.
- Use Cases: PCIe x1 slots are ideal for non-graphics expansion cards that don’t require high-speed data transfer.
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port)
- Overview: AGP was a previous standard for connecting graphics cards, but it’s now largely obsolete. Modern motherboards do not feature AGP slots, and contemporary GPUs are incompatible with this older technology.
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect)
- Overview: PCI slots are also outdated for graphics cards. While they may still be present on some legacy systems, they lack the speed and capabilities needed for modern GPUs.
GPU Compatibility

Ensuring that your graphics card (GPU) is compatible with your motherboard is a crucial step in building a reliable and high-performance system. Understanding these aspects will help you make the right choices.
1. GPU Form Factors
- Full-size GPUs
- Overview: These are the standard-sized graphics cards that you commonly see in gaming rigs. They offer robust performance and often come with advanced cooling solutions.
- Considerations: Ensure that your PC case has sufficient space to accommodate a full-size GPU, and check the dimensions to avoid any fitment issues.
- Compact GPUs
- Overview: Designed for smaller form factor builds, compact GPUs sacrifice some performance for space efficiency. They are ideal for mini-ITX cases and compact gaming systems.
- Considerations: Check your case specifications for GPU size restrictions and power supply capacity to ensure compatibility with a compact GPU.
2. GPU Slot Requirements
- PCIe Compatibility:
- Overview: Most GPUs connect to the motherboard through a PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slot. Ensure that your motherboard has a compatible PCIe slot, typically PCIe x16, for optimal performance.
- Considerations: Check your motherboard’s manual for PCIe slot compatibility and any specific recommendations for using multiple GPUs.
- Slot Width and Length:
- Overview: GPUs come in various sizes, and it’s essential to confirm that your selected GPU fits within the available space in your case. Consider both the width and length of the card.
- Considerations: Measure the available space in your case and compare it to the dimensions of the GPU. Some larger GPUs may have extended lengths or require additional clearance for cooling solutions.
Does it matter if the right slots are for GPU?
Choosing the right slot for your GPU is crucial for optimal performance and compatibility within your system. Here’s a brief understanding of why it matters:
1. Bandwidth and Speed
- The primary GPU slot, typically a PCIe x16 slot, provides the necessary bandwidth for high-speed communication between the graphics card and the rest of the system. Placing the GPU in the correct slot ensures it can harness its full potential.
2. Compatibility
- Different GPUs and motherboards may have specific compatibility requirements. Placing the GPU in the correct slot, as outlined in the motherboard’s manual, ensures that it is electrically and physically compatible with the system.
3. Performance Impact
- Placing a high-performance GPU in a slot with insufficient bandwidth can result in a performance bottleneck. Using the appropriate slot allows the GPU to deliver its intended performance, especially in graphics-intensive tasks like gaming or professional applications.
4. Physical Fitment
- GPU sizes and slot configurations vary. Placing the GPU in the correct slot ensures that it physically fits within the case and doesn’t obstruct other components. This is particularly important when using large or specialized cooling solutions.
5. Multi-GPU Configurations
- For users considering multiple GPUs (SLI or CrossFire setups), using the recommended slots and configurations is vital. Motherboards often have specific guidelines for optimal multi-GPU performance.
Which motherboard slot for the GPU?
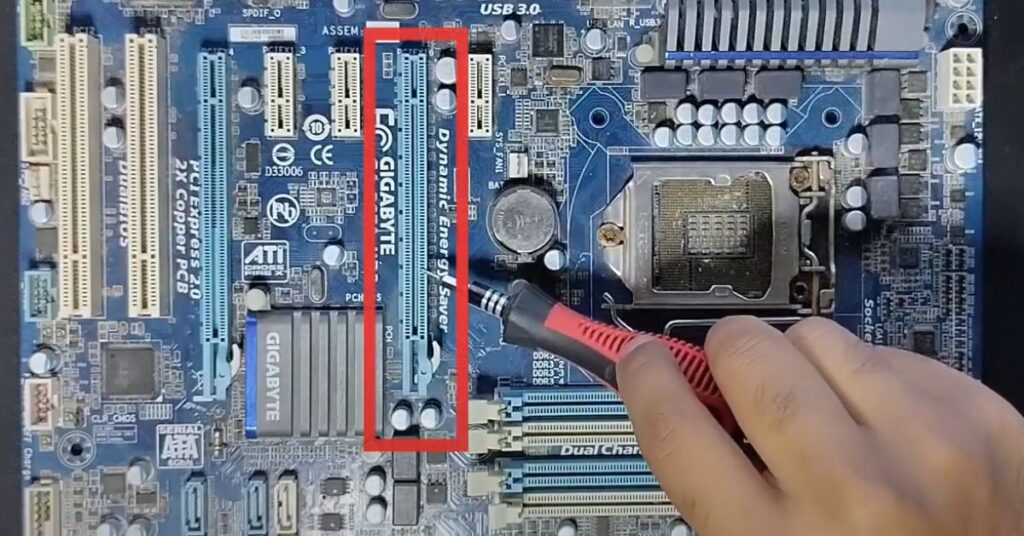

The appropriate slot for a GPU on a motherboard is typically the PCIe x16 (PCI Express x16) slot. This slot provides the necessary bandwidth and speed required for modern graphics cards to operate at their full potential. The PCIe x16 slot is the most common and widely used slot for connecting a GPU to the motherboard.
When installing a GPU, refer to your motherboard’s manual to identify the PCIe x16 slot, and ensure that the GPU is securely and correctly seated in this slot. Additionally, consider factors such as physical space, power supply requirements, and compatibility with the specific graphics card model to ensure a smooth and optimal performance.
What happens if choose the wrong slots?
Choosing the wrong slot for your GPU can lead to several issues, impacting performance, compatibility, and the overall functionality of your system.

Here are some potential consequences:
1. Reduced Performance
- Placing a high-performance GPU in a slot with lower bandwidth than it requires can lead to reduced performance. The GPU may not be able to communicate with the rest of the system as quickly as needed, causing a bottleneck in data transfer.
2. Compatibility Issues
- Some GPUs and motherboards have specific compatibility requirements. Placing the GPU in an incompatible slot may result in electrical or physical conflicts, leading to system instability or failure to recognize the graphics card.
3. Physical Fitment Problems
- Choosing the wrong slot may result in physical fitment issues, especially if the GPU is too large for the slot or interferes with other components on the motherboard. This can lead to difficulty in closing the computer case or potential damage to the GPU or surrounding components.
4. Heat and Cooling Challenges
- Placing the GPU in a slot with inadequate spacing or ventilation can lead to heat-related issues. Graphics cards generate heat during operation, and proper placement is crucial for efficient cooling. Incorrect slot choices may limit airflow and contribute to overheating.
5. Multi-GPU Configurations
- If you’re using multiple GPUs in a system, choosing the wrong slots can impact the effectiveness of technologies like SLI or CrossFire. Some motherboards have specific slots recommended for multi-GPU setups to ensure optimal performance.
6. System Instability and Crashes
- Incompatibility or suboptimal slot choice may result in system instability, crashes, or even a failure to boot. This can be frustrating and may require troubleshooting to identify and rectify the issue.
To avoid these problems, always refer to your motherboard’s manual for guidance on the appropriate GPU slot.
Considerations for Multi-GPU Configurations
When setting up a multi-GPU configuration, such as using SLI (Scalable Link Interface) for NVIDIA GPUs or CrossFire for AMD GPUs, several considerations are crucial to ensure optimal performance and stability.
Here are the key factors to keep in mind:
1. Motherboard Support
Ensure that your motherboard supports the specific multi-GPU technology you plan to use (SLI or CrossFire). Check the motherboard’s manual for information on supported PCIe slots and recommended configurations.
2. GPU Compatibility
Use identical GPUs for the best compatibility. While some multi-GPU setups support different GPU models, using the same model and VRAM capacity is generally recommended to avoid potential issues.
3. PCIe Slot Configuration
Follow the motherboard manufacturer’s recommendations for slot configurations. Some motherboards may support dual x16, x8/x8, or other configurations. Placing GPUs in the recommended slots ensures optimal bandwidth distribution.
4. Bridge Connection
- If your GPUs require a bridge connector (SLI bridge for NVIDIA or CrossFire bridge for AMD), make sure it is properly installed. This bridge facilitates communication between the GPUs and enhances performance in multi-GPU setups.
5. Power Supply (PSU) Capacity
- Confirm that your power supply unit (PSU) can provide sufficient power for multiple GPUs. Multi-GPU setups often require more power, so ensure that your PSU has the necessary wattage and PCIe power connectors.
6. Cooling and Airflow
- Multi-GPU configurations generate additional heat. Ensure that your system has adequate cooling, with proper airflow to dissipate heat effectively. Consider the placement of GPUs to avoid overheating issues.
7. Driver and Software Configuration
- Install the latest graphics drivers and any specific software required for your multi-GPU setup. Configure the settings using the GPU control panel software provided by NVIDIA or AMD to enable multi-GPU support.
8. Game and Application Compatibility
- Not all games or applications benefit from multi-GPU configurations. Some may not support it at all, while others may experience diminishing returns in performance. Check the compatibility of your favorite games and applications with multi-GPU setups.
9. Benchmarking and Testing
- Run benchmarks and stress tests to ensure stability and performance gains with the multi-GPU configuration. Monitor temperatures and system behavior to identify any issues that may arise during prolonged use.
Consider Alternatives
Given the diminishing support for multi-GPU configurations in modern games and applications, consider whether investing in a single, more powerful GPU is a better alternative. Single GPUs often provide more consistent performance across a broader range of software.
Always consult the documentation provided by your motherboard and GPU manufacturers for specific guidance on setting up a multi-GPU configuration.
Common Issues with GPU Slot Selection
1. Performance Problems
- Issue: Reduced GPU performance or lower-than-expected frame rates.
- Solution: Ensure the GPU is installed in the correct PCIe x16 slot with the necessary bandwidth. Update graphics drivers and check for any BIOS updates for improved compatibility.
2. System Instability
- Issue: System crashes, freezes, or unexpected reboots.
- Solution: Verify that the GPU is seated securely in the slot. Check for any physical damage or debris. Ensure the power supply is adequate for the GPU’s requirements.
3. Incompatibility
- Issue: The GPU is not recognized by the system or exhibits erratic behavior.
- Solution: Confirm that the GPU is compatible with the motherboard and that it meets the system requirements. Check for any firmware or BIOS updates.
4. Heat-related Problems
- Issue: GPU overheating or thermal throttling.
- Solution: Ensure proper airflow in the case. Check that fans on the GPU are functioning correctly. Consider adjusting fan curves or adding additional case fans for better cooling.
5. Incorrect Slot Choice
- Issue: Placing the GPU in the wrong PCIe slot.
- Solution: Refer to the motherboard manual for the recommended GPU slot. PCIe x16 is typically the appropriate slot for dedicated graphics cards.
Conclusion
Selecting the correct motherboard slot for your GPU is a fundamental step in building a powerful and stable system. The PCIe x16 slot is the go-to for most graphics cards, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility. Remember, it’s not just about plugging in; it’s about harnessing the full potential of your GPU.
It is important to pay attention to details like PCIe compatibility, slot width, and length whether you’re gaming, working on graphics-intensive tasks, or pursuing a multi-GPU setup. Observe the motherboard’s handbook, take the form factor of your GPU into account, and plan ahead for future upgrades.
In the end, Which motherboard slot for the GPU? is not just a technical query – it’s a gateway to unlocking the visual prowess and capabilities of your machine. So, install that GPU in the right slot, fire up your favorite games, and enjoy the immersive experience your system was built for. Happy gaming!
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use a PCIe x8 or x4 slot for my GPU?
It’s generally recommended to use a PCIe x16 slot for optimal GPU performance. While some GPUs may work in x8 or x4 slots, it can lead to reduced bandwidth and performance.
What if my GPU doesn’t fit in the case?
Ensure that your case supports the length and width of your GPU. Some larger GPUs may require specific case sizes or may not fit in compact cases.
Do all motherboards support multi-GPU configurations?
No, not all motherboards support multi-GPU setups. Check your motherboard’s manual to confirm its compatibility with SLI or CrossFire, and follow the recommended configurations.
Do I need a bridge connector for multi-GPU setups?
For technologies like SLI or CrossFire, a bridge connector is often required to link the GPUs. Check the specifications of your GPUs and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for bridge usage.
Why is my system crashing after installing a new GPU?
Ensure that the GPU is correctly seated in the PCIe slot. Check for proper power connections and confirm that your power supply can handle the GPU’s requirements. Update graphics drivers and check for any BIOS updates.
Can I mix different GPU models in a multi-GPU setup?
While some technologies support mixing GPU models, it’s generally recommended to use identical GPUs for better compatibility and performance.
